

To get Vue SFCs and TypeScript working together, Volar creates a separate TS language service instance patched with Vue-specific support, and uses it in Vue SFCs. This section only applies for VSCode + Volar.
Official TypeScript compiler options docs.If you have configured resolver aliases in your build tool, for example the alias configured by default in a create-vue project, you need to also configure it for TypeScript via compilerOptions.paths. If you're using Options API, you need to set compilerOptions.strict to true (or at least enable compilerOptions.noImplicitThis, which is a part of the strict flag) to leverage type checking of this in component options.
When configuring tsconfig.json manually, some notable options include:ĬompilerOptions.isolatedModules is set to true because Vite uses esbuild for transpiling TypeScript and is subject to single-file transpile limitations.
#WEBSTORM VUE 3 CODE#
app code and test code should have different global variables). Inside the project, we use Project References to ensure correct types for code running in different environments (e.g. The base config is abstracted in the package. Projects scaffolded via create-vue include pre-configured tsconfig.json.
#WEBSTORM VUE 3 FREE#
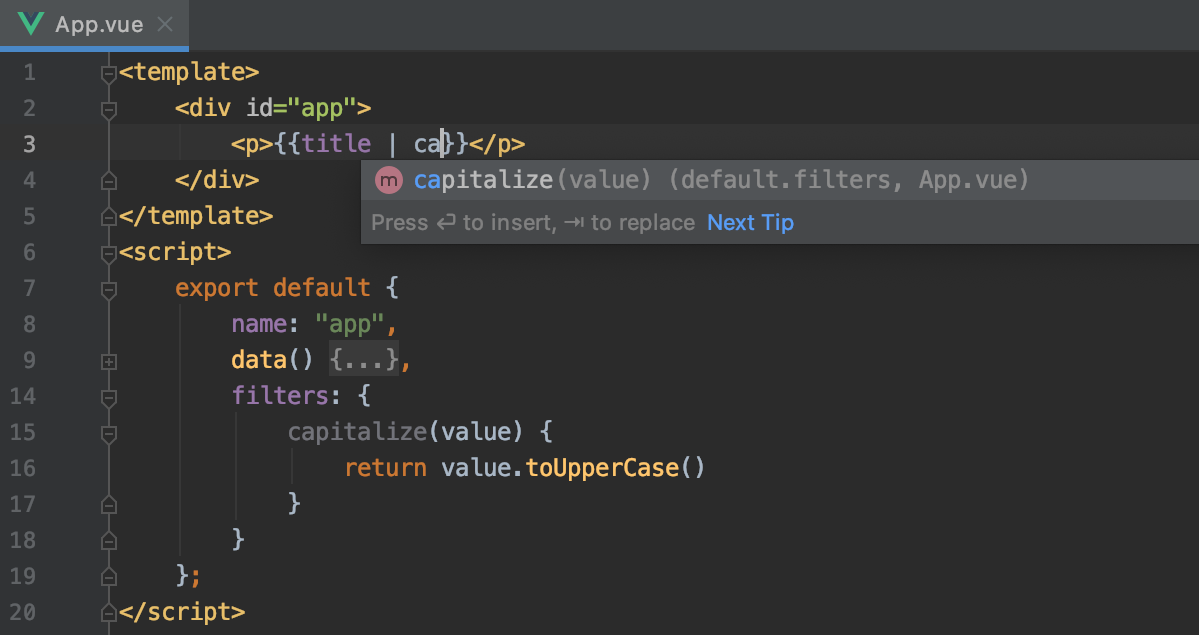
Other JetBrains IDEs support them too, either out of the box or via a free plugin. WebStorm also provides out-of-the-box support for both TypeScript and Vue. TypeScript Vue Plugin is also needed to get type support for *.vue imports in TS files. If you have Vetur currently installed, make sure to disable it in Vue 3 projects. Volar replaces Vetur, our previous official VSCode extension for Vue 2. Volar is the official VSCode extension that provides TypeScript support inside Vue SFCs, along with many other great features. Visual Studio Code (VSCode) is strongly recommended for its great out-of-the-box support for TypeScript. Vue CLI also provides TypeScript support, but is no longer recommended. You can run vue-tsc in watch mode in parallel to the Vite dev server, or use a Vite plugin like vite-plugin-checker which runs the checks in a separate worker thread. It works largely the same as tsc except that it supports Vue SFCs in addition to TypeScript files. vue-tsc is a wrapper around tsc, TypeScript's own command line interface. If using SFCs, use the vue-tsc utility for command line type checking and type declaration generation. This ensures the Vite dev server stays blazing fast even when using TypeScript.ĭuring development, we recommend relying on a good IDE setup for instant feedback on type errors. With a Vite-based setup, the dev server and the bundler are transpilation-only and do not perform any type-checking. Project Setup Ĭreate-vue, the official project scaffolding tool, offers the options to scaffold a Vite-powered, TypeScript-ready Vue project. All official Vue packages come with bundled type declarations that should work out-of-the-box. Vue is written in TypeScript itself and provides first-class TypeScript support. TypeScript also improves developer ergonomics via type-based auto-completion in IDEs. This reduces the chance of runtime errors in production, and also allows us to more confidently refactor code in large-scale applications. Tell webpack what directories should be searched when resolving modules.Ībsolute and relative paths can both be used, but be aware that they will behave a bit differently.A type system like TypeScript can detect many common errors via static analysis at build time. For example, when calling import 'lodash' in ES2015, the resolve options can change where webpack goes to look for 'lodash' (see modules). resolveĬonfigure how modules are resolved. Have a look at Module Resolution for more explanation of how the resolver works. Webpack provides reasonable defaults, but it is possible to change the resolving in detail. These options change how modules are resolved.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
